The Endocannabinoid System: What Is It & How Does It Work?
If you’re a cannabis enthusiast, you’ve likely heard of the endocannabinoid system. Maybe you heard it in passing at a dispensary or stumbled across the term somewhere online. Simply put, the endocannabinoid system is the reason cannabis works.
In this post, we’ll break down those functions and explain their roles. By the end of this page, you’ll have a working knowledge of the chemistry behind cannabis.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
This bodily system is a subsection of the central nervous system (CNS). The endocannabinoid system’s job is to send signals throughout the body. These signals maintain homeostasis, or the unconscious processes that keep you alive. Specifically, the endocannabinoid system deals with immune responses like inflammation. It also plays a part in hunger, sleep, and stress response.
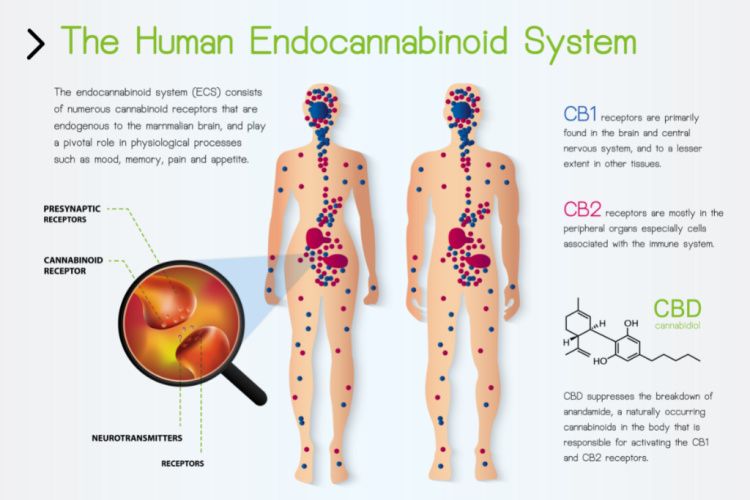
Three main components comprise this system: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. They each play a role in making sure the endocannabinoid system does its job.
Endocannabinoids
The first part of the endocannabinoid trinity is endocannabinoids themselves. These neurotransmitters originate from within the body, hence their name: “endogenous” meaning “within the body,” and “cannabinoid,” like the organic compounds found in marijuana plants.
There are several endocannabinoids that the body creates on command. They bind to endocannabinoid receptors to trigger some kind of response. One of the most common endocannabinoids, anandamide, appears to trigger a “runner’s high.”
There’s one last interesting thing to note about endocannabinoids. While most neurotransmitters simply trigger an “on/off” response in your brain, endocannabinoids work on a sliding scale. As a result, they can cause a much wider range of responses.
Receptors
Receptors are the second part of the endocannabinoid system puzzle. So far, scientists have discovered two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1, which exists throughout the body, and CB2, which are found primarily in the brain.
These receptors’ main job is to bind with endocannabinoids. However, cannabinoids like THC and CBD from marijuana can also bind with receptors, “hacking” them to trigger their normal responses. Remember anandamide, responsible for the runner’s high? Researchers believe that THC may bind to receptors in the same way, tricking the body into triggering the same response.
Enzymes
Enzymes are the unsung heroes of the endocannabinoid system. While endocannabinoids and receptors get all of the attention, enzymes are hard at work behind the scenes.
The endocannabinoid system has its own set of enzymes, separate from the rest of the body. These proteins break down endocannabinoids after the latter binds with receptors. While this may not seem like a big deal, it is.
When enzymes break endocannabinoids down into their constituent parts, your body stores them, ready to recreate them whenever necessary. Without enzymes, the entire endocannabinoid system would break down.
Hacking Your Endocannabinoid System with Cannabis

There you have it: the quick and dirty guide to the endocannabinoid system. This is only a rudimentary breakdown of this complex bodily system, but it will give you a working knowledge of how cannabis functions.
Interested in doing some experiments on yourself (for science, of course)? Look no further than your friendly neighborhood West Hollywood dispensary!